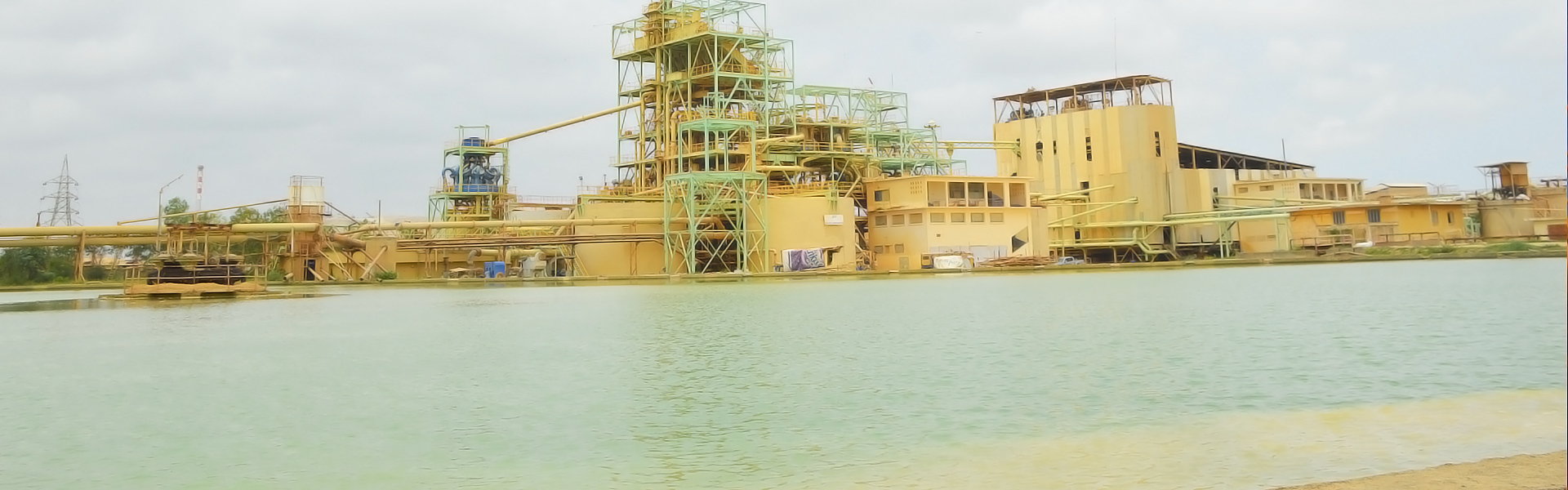
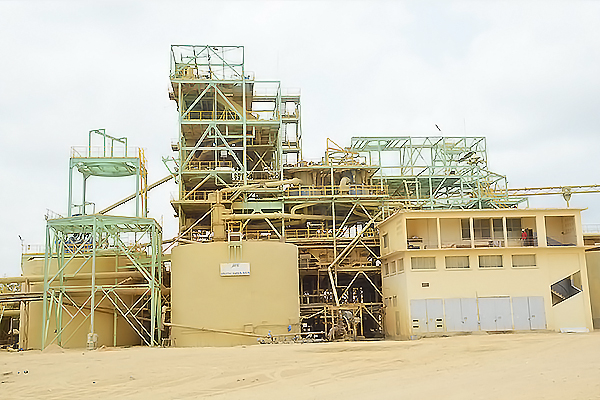
Process
ICS – MINE SITE

History
- 1880:While constructing the rail line from Dakar to St Louis, the geologist H. Hubert discovers the presence of phosphate of lime with phosphoric anhydride. However, the discovery gets published after the First World War.
- 1937:Work of H. Hubert gets published by J. Malavoy, creator of the Geological and Mines Service of French West Africa. The latter resumes research and update the Lam-Lam alumina phosphate deposit near Thiess. His successor, P. Seyer, seeks in France a company interested in the exploitation of the deposit.
- 1942:During the Second World War, the Pechiney Company conducts a geological mission from Oran to Senegal via the Sahara. Research continues and the phosphates of Thiess are beginning to get developed. In 1944, the General Director of the O.F. Mines, Gilbert Arnaud, discovers a deposit of phosphate of lime near approach road of Cayar.
- 1945:The presence of deposits of phosphate of lime in the zone of Taïba N’Diaye is checked again. The BRGM (Bureau of Geological and Mining Research) and SERMIS (Senegal Mining Research and Research Society) undertake systematic exploration.
- 1948 – 1949:confirmation of the deposit of phosphate of lime, Taiba by The Bureau of Mining France Overseas (BUMIFON)
- 1952:BRGM and the SERMIS create a company of studies and set up a pilot unit.
- 1953:A pilot excavation gets started
- 1957:Creation of the Compagnie Senegalaise des Phosphates de Taïba which begins the exploitation of the deposit with installed capacity 600,000 tonnes.
- 1960: Commissioning of Laverie (Preparation, flotation, drying plant). First tonne of Rock Phosphate Concentrate produced
- Aug 10, 1960:First ship loaded with phosphate gets shipped to Japan from Dakar
- Aug 20, 1970:Commissioning of the first Pre-treatment Plant at Ndomor. (from 1960 to 1970 running of a Floating Pontoon) and increasing the capacity to 1.2 MTPA
- Oct 20, 1980:Commissioning of a new Pre-treatment Plant in Keur Mor Fall (with the movement of mining from Ndomor Diop to Keur Mor Fall) and capacity gets increased to 1.80 MTPA
- 1984:Starting of Industries Chimiques du Senegal (ICS) for phosphoric acid production
- 1996:Merger of CSPT and Industries Chimiques du Senegal (ICS).
- 1999:Implementation of scheme for doubling the phosphoric acid plant capacity
- 2001:2nd unit of phosphoric acid plant start-up
- Oct 2003: Opening of the new mining panel Tobene
- May 8, 2004:Commissioning of Scalpage Plant and Tobene Conveyor belt
- Apr 29, 2008:Recapitalization and IFFCO led consortium takes over ICS
- 2014:Indorama Group takes over ICS
Location
The mine site is located ~100 km north of Dakar. It is well connected by road. A rail line connects the mine site & Dakar port for transport of Acid, Sulphur & concentrate.
Mining Concessions & Permits
ICS holds three contiguous Mining Concessions covering an area of around 300 Square km near Mboro in Thiess region and one permit for prospecting & exploration at Gossas.
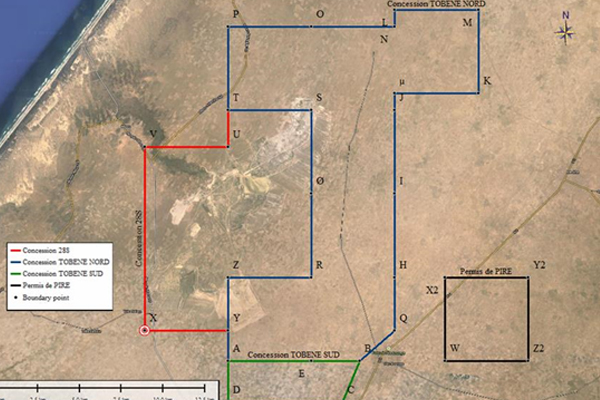
Exploitation of Tobene panel commenced from 2003.
Exploration to establish the Geological Resources is in progress in Pire Goureye, which is a part of the ICS Mining Concessions.
Currently exploration is under progress in Gossas Permit.
Geology
The phosphate beds are part of a very extensive phosphate-bearing area of northeast of Dakar. Phosphate mining takes place mainly in the Taiba concession.
Reserves
The ore body thickness and quality are well defined by the exploration programs.
Reserves in Tobene mining panel are more than 50 million tons of Rock Phosphate concentrate under Proved and Probable categories.
In addition to the reserves in Tobene panel, more than 100 million tonnes of resource has been identified within the mining concession. Systematic exploration is planned within the strategically prioritized areas for converting the Geological Resources into Mineable reserves category.
Method
The mineral is excavated by Open cast method of mining. The Overburden layer of sand and clay is divided into 3 benches and removed by different combination of machineries. The Level – 1 Overburden is removed by Bucket Wheel excavators and conveyor system; Level 2 by shovel and dumpers and in Level-3 the OB cover over the mineral is removed by the Draglines. The Phosphate mineral is excavated and loaded onto dumpers by the draglines or after side casting by dragline, it is re-handled and transported to the pre-treatment plant.
Backfilled area is brought back to near ground level.
The mining activity is supported by a good fleet of ancillary equipment.
Beneficiation plant
Scalping Screen plant:
The Silex (Flint stones) are removed by the scalping screen and disposed near the plant. The particles less than certain size are carried to pre-treatment plant by a belt conveyor and fed to the pre-treatment plant.


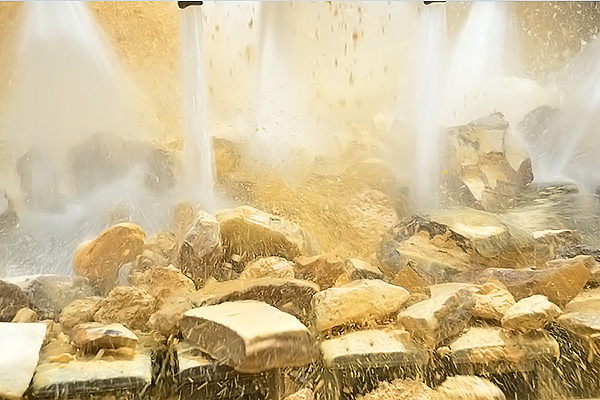
pre-treatment plant
This is a wet processing plant. The feed is screened in different stages of screens under high-pressurized water. The mineral gets scrubbed by a scrubber for removing the useful mineral attached to the rocks. The remaining silex are removed and transported by conveyor and dumper and disposed. The mineral particles are collected and pumped towards the preparation plant for further treatment, through a basalt coated pipeline.


Preparation
The minerals received from pre-treatment are first screened. The larger particles are ground using rod mills and screened in a closed circuit. The particles under certain microns and the slimes, are removed by cyclone and sent to slime thickeners. The overflow of these thickeners is recycled. The underflow of thickened slime slurry is pumped to slime pond (old mine area), which still contains P2O5. Presently old slime ponds are used for agricultural activities. ICS is studying to unlock this economical value of these slimes.
The last stage of the treatment consists of sizing of the remaining ore. This leaves two products:
- The Fines
- The Coarse
These two products are the feed to the flotation plant.
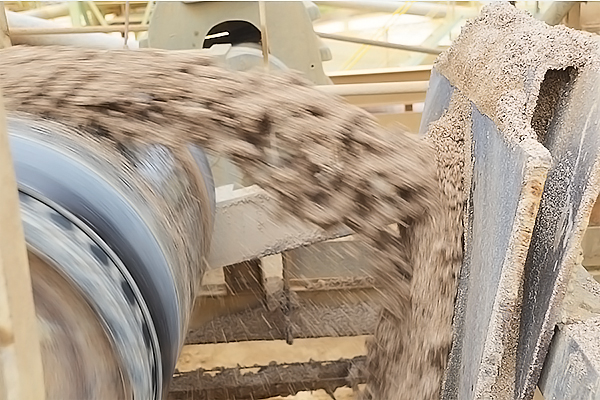



Flotation
The plant has three flotation circuits namely, the coarse one, the fine one and the scavenging one.
The concentrate is dewatered by filter belts. The concentrate is stocked for later feeding to acid plant or to the Darou acid plant by conveyor. The previously rejected tailings which are still good grade, are taken and processed in the scavenging circuits. The tails of the flotation are pumped towards the tailing dam.
Recovered water from slime pond and tailing dam are brought back to plant.



Water Conservation Initiative
Through Paste Thickener project implemented in April 2020, help recover water from slurry. Water recovery increased to 89%. First such initiative in ECOWAS.


